Search engines rank content on the web based on users’ search queries. It is an online tool that conducts search for websites based on user’s query. The sole objective of a search engine is to provide relevant results that are useful and match the search intent of the user.
In this post, we will cover how search engines work and generate results on SERPs. Understanding the working of search engines can help you in improving your site rank on search results and garner more clicks.
Page Contents:
How does Search Engine works?
A search engine is an online tool that performs website search on the internet based on user’s query. It is used to access websites and pages from the web. They find out results in their own database, sort them and prepare an ordered list of these results known as search engine results pages (SERPs).
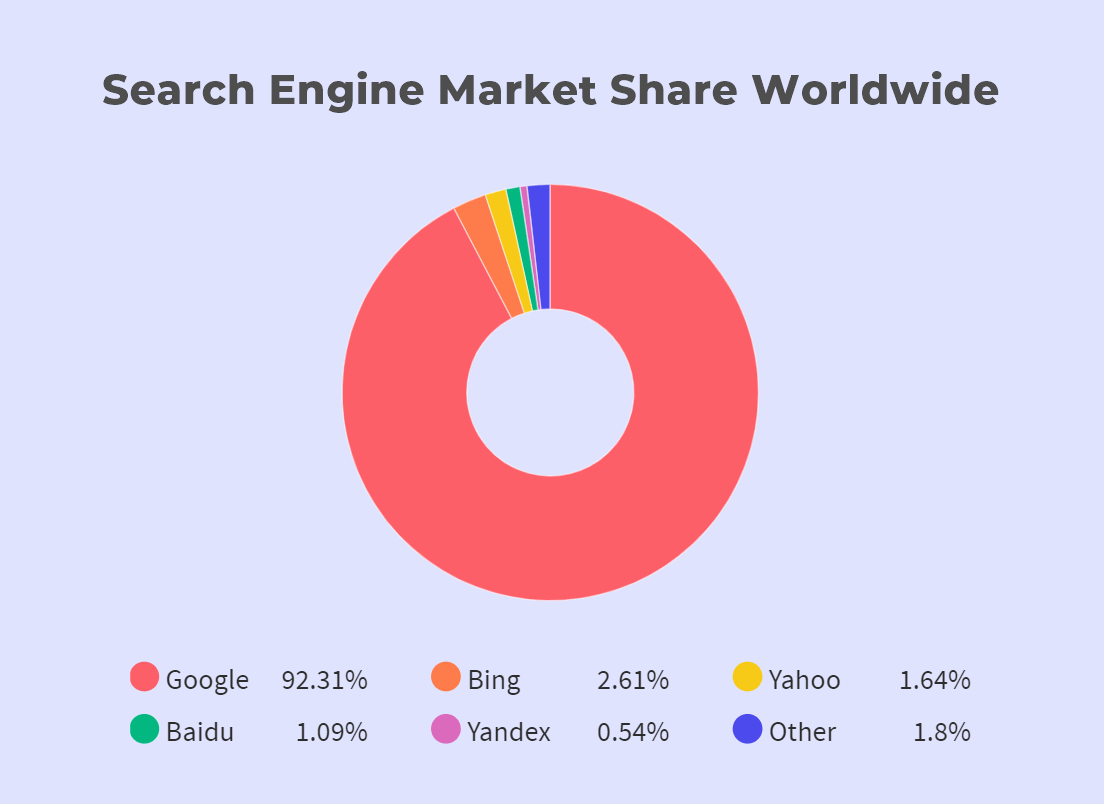
Google is the most popular search engine in the world and has been number one for years. Other commonly used search engines are Bing, Yahoo, and Baidu.
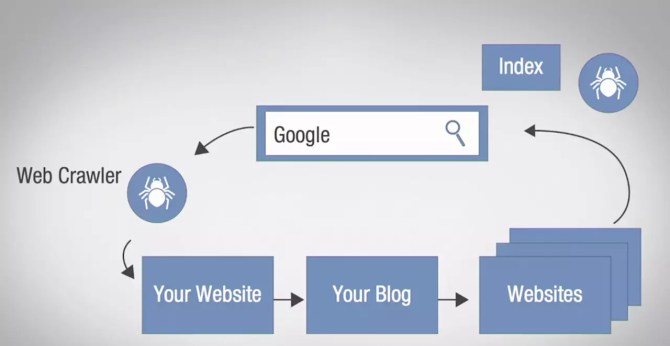
There are three main steps that describe how search engines work:
Crawling
The process of finding new web pages on the internet starts with Crawling. Search engine has a number of computer programs known as crawlers that find information on the web. The search engine bots crawl more than 130 trillion web pages.
Crawling is a process in which search engine crawlers visit each website and download the pages. Search engines continuously look for new web pages to add them to the index. Search engines crawl webpages based on factors such as:
- Page rank of the URL
- Whether the URL is new or old
- Frequency of URL change
Crawlers scan the web for information using algorithms that determine which pages to crawl, and the frequency of crawling. Crawlers visit each site through tags HREF and SRC and create a map of interlinked pages. They find out how many pages a site has and whether it has the text content, images, videos, or other formats (CSS, HTML, JavaScript). They also keep a track of any updates made to a site such as link updates, pages added or deleted, and other changes made to a website.
Ensure that your website is easy to find and crawl. You can follow the guidelines below to improve accessibility for crawlers:
- Site hierarchy: Follow a logical site hierarchy that goes from domain to category to sub-category. This enables crawlers to identify and crawl your site in a much faster time.
- Links: Crawlers move between different pages using internal links. Make sure to include them to make your site easy to crawl and index.
- XML Sitemap: XML Sitemap is a list of all your website pages that serves as an instruction manual for crawlers. Plugins like Yoast SEO and Google XML sitemaps are useful in updating the sitemap whenever a new post gets published.
Indexing
Webpages discovered by search engine bots during the crawling process are added to a database known as index. The process of storing webpages into a search engine database is known as indexing. Index is basically a huge library of all websites. It is a massive list of sorted web pages that search engine crawlers scraped from the internet.
Once a search query is entered in the search field, the most relevant results are picked from the index and are displayed on the SERPs. When a user types the query in the search field, the results are matched from the index. All the pages are identified from the index and arranged in a hierarchical order of their relevance.
Your website has to be indexed in order to appear on SERPs. If the webpage is not present in the index, search engines won’t be able to find them.
In addition to the search query, the factors which influence ranking on search results are:
- Location: Queries with keywords such as ‘near me’ ‘shop timings’ are location-dependent.
- Language: Results may vary depending on the user’s language if it gets detected.
- Device: The results that appear on SERPs may also vary based on the device used for searching a particular keyword.
- Search history: The users’ previous purchase history may also impact the rankings on search results.
Cases when your webpage URL is not indexed:
In some cases, your URL may not get indexed by the search engine. It can happen due to:
Robot.txt file: If a file states that your page should not be visited by search engines. You can control access of the crawled pages using a robot.txt file.
Canonical tag of noindex tag: Noindex tag signals search engines that your page should not be indexed. Canonical tag indicates search engines to index another similar page instead of the current one.
Low-quality: If your page has duplicate, low-quality content, then it may not be indexed by search engine algorithms.
404 error: If the URL is returning a 404 not found error, then your webpage will not get indexed by search engine bots.
You can use the URL inspection tool to monitor which webpages crawlers are viewing on your site. This tool also provides information on why crawlers are not indexing a particular webpage and generate request to index those webpages.
Ranking
When a user performs an online search, search engines scour its database for the most accurate results and rank the results based on the website’s popularity and relevance.
The results which appear on search engine result pages are based on the search query and best possible match of users’ search intent with the keyword entered. Search engines sort the right results from the indexed database to return specific answers to each query. The ranking is determined by various parameters such as relevancy, location, quality, authority, etc.
Search engines help in improving the visibility of your company, resulting in more leads and revenue. Almost everyone uses a search engine to get answers to their questions, product suggestions, and course information, among other things.
One of the most important aspects of a successful SEO campaign is understanding how search engines work. If you are a business owner, website developer, designer, or marketing expert, you will benefit from understanding how search engines work. Visit Serpok to know more.